The principle of operation of a Bicycle transmission
Bike transfer: an Explanation for beginners

If you don’t know how many gears your bike how much you really need or even do not know how to use them correctly, don’t worry — you are not alone. Therefore, in the present, not quite standard for automobile magazine material, we’ll try to explain in simple words how does the system of gear on the bikes, what are the facts about her you need to know and why the Bicycle transmission in something similar to a car transmission. So, let’s take a closer look with all these switches, sprockets and chains, because it is through them that you bring your bike in motion. Of course, if you have one.
Understanding of the basics of Cycling gear, and how changing the size of the stars on the front and back of the cassette will affect your pedaling (simple – pedaling), will help you choose the most appropriate gear ratio for your fitness level and to adapt to a difficult section on the track.
If the car you’ve got before the bike, the task of choosing two-wheeled sports equipment or vehicles for joyrides may not be as easy as it may seem at first glance. The goal in fact absolutely trivial.
Moreover, when choosing a bike you need to start to determine the direction of its use, the so-called riding style, and these styles these days have multiplied so much, that you can get confused. Just a great set! It can be like riding on the highway for a racing or semi-Pro bike race over rough terrain on cross-country bikes, a variety of extreme types of Cycling or simply walking the use of urban models for men (boys) and women (girls) of all ages.
For each of these models and areas of use will apply diverse type transmission, from the simplest single-speed (the same principle of action, what was on the Bicycle the “Ural” and the like simple “old men”) to various versions of the Multispeed chain gear. Why are these mnogozvezdochnogo switches on bikes, how they work and what type of drive would be better? Let’s see.*
*We’ll touch on only the basics of Cycling transmission. Pereiro like a belt full of drives and such types of transmissions: Here is the most effective Bicycle transmission in the world, to touch will not specifically.
Bike transfer: basics
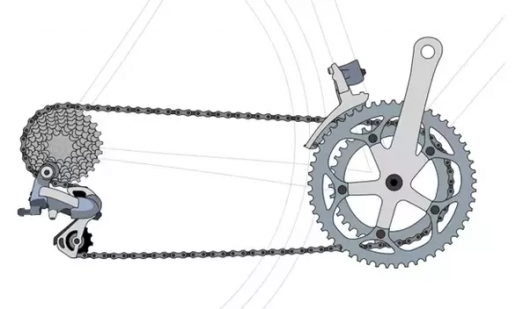
How many speeds on my bike?
Start exploring Bicycle drivetrain with the basics, namely? with the number of speeds. How to determine or calculate how many speeds on a bike? The task for the first class school cyclists. The number of speeds the bike is very easy to calculate, it is enough to multiply the number of stars behind their front number. Thus, if the front you have three stars (some cyclists call this element “chaining”, the essence remains the same), a rear mounted cassette for 10 stars, your bike has 30-speed transmission. In other words, when driving you can use each of the ten rear sprockets in combination with each of the three chainrings.
The simplest algorithm suitable to calculate any multi-speed bike gear: 2 front star behind 11 – the bike 22 speed, and so on.
Why you need a multi-speed drivetrain on the bike?

And why do we need such a large set of stars? 30 gear, not a lot? Car only 10 MB and then problems happen. If the answer is in two words, the need in a particular gear directly dictated by the riding style and sports applications. Such a wide range of gears allows cyclists-athletes to maintain a comfortable pedaling rate (called cadence the number of revolutions of the pedals per minute that a cyclist makes while riding), regardless of gradient or terrain — something that can not give none single-speed chain transmission.
High transmission, sometimes called cyclists “a great program”, which is optimal when descending or riding at high speeds. The tallest, or the biggest gear on the bike is selected by combining the very large size of the chainring from the most compact for the number of teeth of the rear sprocket. For example, can be expressed using the value “53×11”.
On the contrary, the combination of the smallest front gear with the largest rear sprocket will give access to the lowest available gear, which will help you not straining to pedal, even on very steep climbs.
Let’s just clarify one thing — the presence of a large number of gears means that the bike would be faster. Dynamic – Yes, faster – no! A bike with 30 or more gear is not an indicator of a machine designed to beat the land speed record and bypass speed bike with one gear, provided that these bikes use the same gear ratios.

A large amount of gear can help you go up and down a hill, but faster from them, you not going
We are talking about the effectiveness and availability of a much wider range or gear selection for the situation at hand with which to fight on the track or on the roads. Just as cars, bicycles win in dynamics from start in low gear when accelerating from rest or when climbing a steep hill, with a multi-speed transmission allows you to achieve maximum speeds without excessively high speed as the set maximum speed can be switched again into high gear.
Continuing the comparison of the bike with a car, we can say that the use of very low transmission at high speed will lead to high fuel consumption of the latter. The same applies to pedaling a bike. Going too fast to pedal quickly run out of steam. There’s only one conclusion – the more gears in the transmission, the greater the opportunity to find the right gear for a specific situation, speed and cadence for a comfortable, efficient and safe ride.
In a broader sense, during the reign of the 5 and 6-speed cassettes, the range of 12-25 teeth in the stars is achieved by adding a significant amount of teeth on each rear gear, which led to a rapid change in loads. In such systems lacked the smoothness of the shift and continuity of progression. Modern 10 and 11 speed cassettes solve this problem. Therefore, it is more comfortable, more convenient and these systems wear out more slowly.
Why do some people choose a single speed bike (singlespeed)?

Interestingly, in our age of development of various technologies gear bike (the examples we give below), some people prefer to use single speed transmission, the so-called “singlespeed”. These bikes have only one gear, matched a certain ratio of the star – front and back. Proper selection of the ratio of the teeth allows a lot faster to start and accelerate to a maximum velocity of 30 to 34 km/h.
Single speed bikes are popular among melomanov living in lowland areas, moving on their two-wheeled iron horses exclusively in the city or engaged in extreme kinds of Cycling, the so-called “stunt bike”.
Plus at this single speed bike is also a lot of:
1. Cheapness. Indeed, to collect the single speed bike is much cheaper. How? Everything will depend on the level of components. If you take really high quality racing components to the highest level in the line Shimano – XTR, will look roughly as follows (counting the cost of the components of a multi-speed bike):
I. System Shimano XTR 11-speed – on average, 25,000 rubles
II. The carriage of a high level (it includes the bearings, a housing with a thread fit into the frame) – about 3,500 rubles
III. Star front (Shimano XTR) – 5 thousand rubles
IV. Circuit level XTR 11-speed – 3 thousand rubles
V. Rear derailleur XTR from Shimano – 15.000 rubles for discounts, cost them in a season can reach up to 22.000 rubles
VI. But still need the so-called “lever” – the shifter (about 6,500 rubles), ropes, shirts and of course the rear cassette, which also is not cheap – 5 thousand roubles.

Total just for the transmission will take about 63.000 rubles! Yes, it’s the alignment of the prices for really high quality components racing level. They are durable, easy, great working, and so on. But for the same money you can buy the whole bike tricks on no less quality and much more durable components with a single transmission. Feel the difference?
2. Reliability. You know what impresses a Kalashnikov? No, not marksmanship at long range. He just practically trouble-free in harsh operating conditions. Also single-speed bicycles. There’s just nothing to break! Remember the old Soviet bikes that you, for once, must have seen in the Outback. They serve their masters for decades… No wonder thrill-seekers around the world almost always use the bike “singlepid” for their tricks.
3. Maintainability. To repair a bike with one gear a snap. And parts are inexpensive. You can not say about the “multipede”. Even if you take the average price range of the acceptable reliability of the components, such as Shimano XT or SRAM X9, but it’s still not cheap, one rear derailleur, one of these manufacturers will give you 6 thousand rubles.
4. Racing ambitions. You will be surprised, but even racers sometimes use one-speed transmission. They do this to reduce the weight of the bike (all the extra attachments, no matter how slight it may be, still has weight) and to eliminate the risk of problems with shifting. In this case, the selection of the correct ratios is crucial.
5. Finally, a track bike has only one gear. It’s not an advantage, just a fact.

As a result, with correctly chosen ratio, the cyclist gets a smoother, more accurate pedaling without difficulty at the time of moving the chain to a larger or smaller sprocket. And that means pedaling in certain modes of driving will be more effective.
Win some, lose some

If you have never been interested in Cycling theme, you’ll probably be surprised that it turns out that despite the presence of such a large number of programs on each of them and you need to go.
Reality Multispeed transmission is such that the “overlap” of certain bands in a certain combination of stars is almost inevitable. For example, with 33 assists, such combinations of stars as 53×19 and 39×14 – it’s the same transmission.
Also you can’t use, at least permanently, the extreme series of stars on the diagonal. For example, the extreme left chainring and small, far right sprocket on the cassette. Such misalignment will create excessive chain tension will increase the wear of the teeth of stars, there will be overload on the spring legs of the rear derailleur.
The old advice is still relevant – avoid “crossing the chain”. Cm. the left drawing to illustrate it:

Also one of the tips, which will help to keep expensive component as long as possible – avoid shifting in the middle of the climb. This creates a very heavy load on the transmission, switches and circuit. To avoid problems, make the switch prior to starting to overcome bias.
Thus, you don’t always get 33 transfer at their disposal and may not always be able to use them. Actually this cannot be called a marketing ploy of deloproizvodstva, just such a technological flaw initially is the shift pattern of the bike. From him nowhere to go.
Moreover, the total number of assists is not an end in itself, much more important is the bike to have a continuous progression that can be achieved closely spaced gears on the rear cassette.
What are the different types of gear?
Nowadays there are a lot of options led transmissions, so find the right option for your led classes is not difficult. Go over the basic types of transmissions.
Standard double
Two stars in the front paired with 11 sprockets at the rear. Standard dual scheme is usually the preferred choice for racing, offering the largest stars in the front to maintain a high speed.
A triple scheme
Getting three leading stars, you get the option to switch to the small chainring. When throwing a chain on the larger rear sprocket, you get a bike-terrain vehicle, able to climb on very steep climbs.
Compact
Compact version of the transmission of the first type. Both front stars small, usually 34-36 internal teeth, external teeth 48 and 50. Very popular today scheme for Amateur athletes, not allowing to reduce the cadence, even on steep climbs.
Singlespeed
Here everything is clear. Two stars, one parcel. No switches and other “extra” parts.
Planetary hub
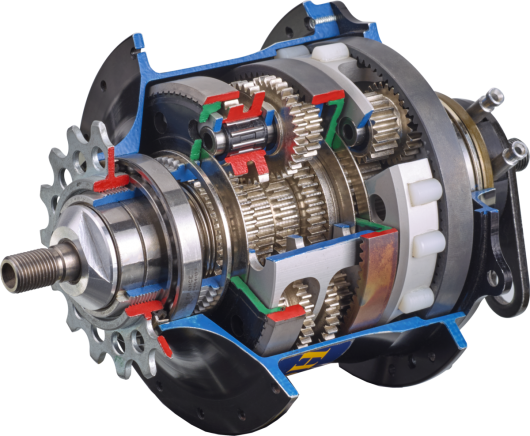

Technically difficult, heavy, expensive and difficult to service (though often subservient and not asking) element of the transmission, more like the variable speed box on cars. Switching occurs without external “periklutos” and other auxiliary machinery. At this moment in the market there are two, four, seven, eight, nine, twelve speed hub gears from SRAM, Shimano and Sturmey-Archer. There is even a 14-step “planetary” from the company Rohloff. The cost of one volacci unpleasant surprise – about 90 thousand roubles.
Suitable for walking a bike than to race.
Dictionary of Cycling terms
“Chainring” (the forward star): toothed ring at the front of a chain drive attached by bonok (studs) or bolts to the connecting rod of the actuator.
Cassette: a group of stars on the back of the transmission. Can contain a different number of stars, mostly from 7 to 11 different sizes (different diameter and number of teeth). Mounted on the drum rear bushing.
Block stars ratchet: another term for a rear sprocket. He, in fact, refers to the older technology, in which the drum ratchet are in the cassette, which, in turn, is screwed onto the hub axle.
Switches: front and rear switches do all the hard work to move the chain from one sprocket to another.
Asterisk: refers to a single transfer to tape/rattle.
Ratio: describes the ratio between the sprockets of the rear cassette and front stars. For instance, “53×12”, or stars on the cassette (11-25).
“t” stands for “teeth” – teeth (on the sprocket). Is used to denote the number of teeth on the star, for example – ‘ 23t’.

Effective use of gears, Cycling will help you to easily and safely climb the mountain
Transmission: the term that groups in a single system all moving parts, uniting the connecting rod with the rear wheel and hence driving the whole bike through chainrings, chain, cassette and switch.
Cadence (pedalling): the pedaling speed per unit time, measured by the number of revolutions of the crankset per minute.
STI lever: short for “Shimano Total Integration” is a term that refers to the Shimano design that combines the brake and shift levers for road bikes. Sometimes the term is applied to the switches/brake levers regardless of brand.
Ergo lever: Brand company name Campagnolo, specializing in the production of attachments for road bikes. Branded version of the integrated shift and brake levers.
DoubleTap lever: SRAM is a piece of cake, from the point of view of switching technology, which uses the same lever for up and downshifts.
