Signs of malfunction of the camshaft sensor
What happens if you wear out the camshaft position sensor.

This can happen at any time without notice. Imagine You are driving on a highway, moving at high speed, and then suddenly the car engine shuts off. After you experience unpleasant moments associated with disabling the power steering and the deterioration of the braking system, you are parked on the sidelines will wonder what happened to the car. A frequent cause of sudden engine shutdown while driving is failure of the camshaft sensor (camshaft position sensor).
Sometimes the camshaft sensor (CMP) can fail without warning, causing the engine stalls. In some cases the driver may not know about the problems with the sensor as long as when you start the engine refuses to run.
In this article we consider the main symptoms of camshaft position sensor and will tell you what to do to rectify the fault. But first let’s learn what makes this gauge in a car.
What is the camshaft position Sensor (CMP)?
In the cylinder head of the engine of your car is one or two camshafts, which feature petals required to operate the intake and exhaust valves. The crank is in the block, which, receiving the torque from the motion of the pistons in the block, passes it through gear, timing chain (or timing belt) on the camshaft.
In order to determine which engine cylinder is in tact, your car’s computer monitors the position of rotation of the camshaft relative to the crankshaft position with the camshaft sensor (CMP). The information received from the CMP sensor, is required to configure synchronization feed the spark to the combustion chamber and fuel injectors. Thus, the camshaft sensor directly affects the fuel consumption of cars and the amount of emissions in the exhaust.
The most common sensors camshaft: magnetic and is based on the Hall effect. Both types of sensors transmit a voltage signal to the electronic engine control unit or onboard computer of the machine.
Magnetic type sensor camshaft produces its own alternating current (sinusoidal wave). Typically, this sensor has two wires. The sensor is based on Hall effect uses an external power source for receiving a digital signal, and usually has three wires.
Depending on the brand and type of your vehicle your engine may have one or more camshaft sensors. Also your car can use two types of CMP sensors.
Symptoms of a faulty camshaft sensor
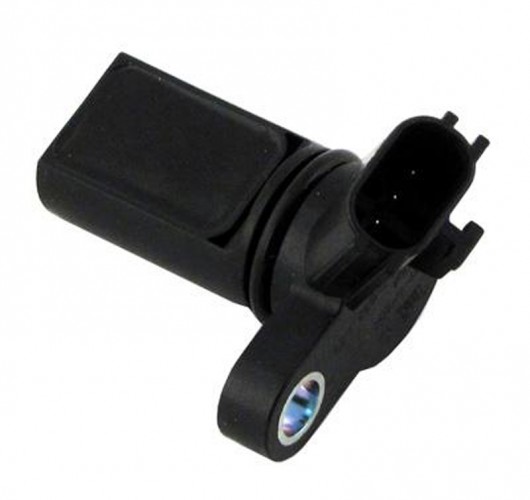

As well as any part or component of your vehicle, the CMP ultimately will sooner or later stop working due to wear and tear. This will happen in any case, once expired its maximum service life. This usually occurs due to wear of the inner winding wire or associated component.
Usually in this case your engine may begin to work intermittently, and the symptoms can vary depending on the type of sensor wear. For example, the sensor may wear down the connector, the internal circuit of the sensor or fail the associated component.
 – On some vehicles, if there is a fault in the camshaft position sensor, transmission may be blocked in a single transmission, until, until you turn the engine off and again it will not start. This can be repeated with a certain periodicity.
– On some vehicles, if there is a fault in the camshaft position sensor, transmission may be blocked in a single transmission, until, until you turn the engine off and again it will not start. This can be repeated with a certain periodicity.
 – If the camshaft sensor during movement of the vehicle begins to not work properly, you can feel that the car stutters losing speed.
– If the camshaft sensor during movement of the vehicle begins to not work properly, you can feel that the car stutters losing speed.
 – In case of sensor failure the camshaft , you may encounter a noticeable loss of engine power. For example, your car can’t accelerate above 60 km/h.
– In case of sensor failure the camshaft , you may encounter a noticeable loss of engine power. For example, your car can’t accelerate above 60 km/h.
 – The engine can stall intermittently due to a faulty CMP sensor
– The engine can stall intermittently due to a faulty CMP sensor
 – In case of failure of the sensor you will notice poor performance of engine: loss of dynamism, misfires when the ignition is on, pushing under acceleration, popping in the exhaust system, etc.
– In case of failure of the sensor you will notice poor performance of engine: loss of dynamism, misfires when the ignition is on, pushing under acceleration, popping in the exhaust system, etc.
 – On some car models with faulty camshaft sensor can completely disappear the spark that will eventually lead to failure of engine start.
– On some car models with faulty camshaft sensor can completely disappear the spark that will eventually lead to failure of engine start.

After your car’s computer detects a malfunction of the camshaft position sensor, it usually will result on the dashboard indicator “Check engine” (Check Engine). Immediately after the discovery of poor performance of the CMP sensor, the computer will record in its memory the error code of the sensor. In order to accurately determine the cause of the malfunction of the camshaft sensor, it is necessary to conduct computer diagnostics of the car, connecting the special equipment to the diagnostic connector of the machine. Then, using a special computer program to read the error code. Below we present you a table of diagnostic error codes that are associated with the wear of the camshaft sensor.
Error codes camshaft position sensor CMP
P0340 CMP
There is no signal from the camshaft sensor
P0341 CMP
Incorrect phase distribution
P0342 CMP
Low voltage sensor circuit camshaft
P0343 CMP
High voltage sensor circuit camshaft
p0344 CMP
The location of the camshaft sensor in the car

As you can probably guess the specific location of the camshaft position sensor varies depending on the brand and model of the vehicle. In most cars you can find a sensor somewhere around the cylinder head. Look for a sensor around the top of the location of the timing belt or protected parts of the wiring in the front of the engine.
Also, the sensor may be located at the rear of the cylinder head.
Some car models can have a special compartment under the hood, which has a camshaft sensor (for example, in some cars manufactured by General Motors).

Additionally, some car models camshaft sensor can be located inside the cylinder head.
If necessary, check the user manual of your vehicle to know exactly where is the CMP sensor. If you don’t have a repair manual and service your vehicle, you will be able to find it online or buy at a car shop where a large selection of cars such literature.
We strongly encourage all car owners to buy such book (a guide to repair and maintenance) specifically for your mods and car model. Manual car will help you in case of breakages and malfunctions, and will be a valuable reference for performing scheduled maintenance of vehicle and minor repairs.
Troubleshooting sensor camshaft (CMP)

If your car’s computer has detected a sensor error and is already included on the dashboard icon “Check engine”, you can easily find out the error code which resulted in display on the collection tubes. For this we recommend each driver to purchase an inexpensive set of diagnostic equipment for computer diagnostics. If you can’t afford to buy a diagnostic scanner for car, contact any cheap service, where you think the errors in the car computer.
After you by error code found out that in your car there is a sensor malfunction camshaft or related components, you should do some simple tests. Remember that a DTC indicating a potential failure of the camshaft position sensor, does not necessarily mean failure of the CMP sensor. It is possible the cause of the fault is not in the sensor and the sensor connector is damage or wires connected to it. Or perhaps out of order related components of the vehicle.

However, in order to establish precisely does normal camshaft sensor, you may need to spend a small amount of diagnostics. Especially it is necessary to consider that in some cases, in order to test the effectiveness of CMP signal may need special equipment, without which it is difficult to establish the cause of the fault.
However, you can do a few simple checks yourself, using a digital multimeter (DMM):
 – First, check the camshaft sensor electrical connector and wires condition. Disconnect the connector and check it for any signs of rust or contaminants. For example, fuel. All of this can hinder good contact for the transmission of electricity.
– First, check the camshaft sensor electrical connector and wires condition. Disconnect the connector and check it for any signs of rust or contaminants. For example, fuel. All of this can hinder good contact for the transmission of electricity.
Then check for damaged wires: broken wires, signs of the wires melting from the nearby hot surfaces.
Also, make sure that the wires to the camshaft sensor do not touch spark plugs or ignition coils which can cause interference and prevent the sensor to transmit the correct signal.
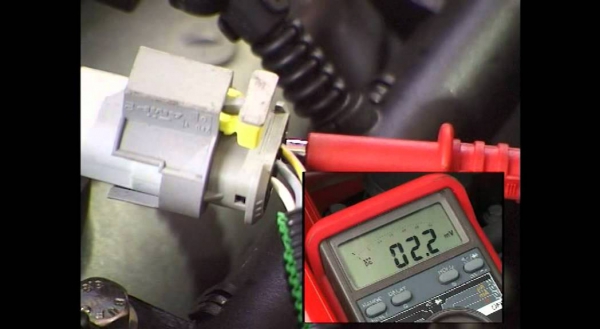
 – After the above checks, use a digital multimeter that can test AC current (AC) voltage or direct current (DC) – depending on the specific type of camshaft sensor that is used in your car.
– After the above checks, use a digital multimeter that can test AC current (AC) voltage or direct current (DC) – depending on the specific type of camshaft sensor that is used in your car.
Also before you test you need to set the DMM to the correct electrical parameters for a particular sensor type SRM. Usually this information is specified in the repair manual and maintenance of vehicles.
 – Some sensors camshaft allow you to create splitter electrical circuit of the CMP sensor in order to read the signal from the sensor during its operation in the car.
– Some sensors camshaft allow you to create splitter electrical circuit of the CMP sensor in order to read the signal from the sensor during its operation in the car.
If the type of your sensor allows you connect up the leads of the multimeter, you can unplug the connector from the sensor, attach a copper wire by inserting it into each connector of the sensor.
Then plug the connector back to the sensor, being careful not to short the wires while testing. If you use this method, tape the wires with electrical tape.
Testing two-wire sensor camshaft

 – If in your car the camshaft sensor has two wires, it means that the automaker installed on the machine magnetic type of CMP sensor. In this case, set the DMM to “AC voltage”.
– If in your car the camshaft sensor has two wires, it means that the automaker installed on the machine magnetic type of CMP sensor. In this case, set the DMM to “AC voltage”.
 – Have an assistant turn the ignition key without starting the engine.
– Have an assistant turn the ignition key without starting the engine.
 – Now check the availability of electricity which must flow through the sensor loop. Take one contact of the multimeter and hold it to ground (any metal part on the engine). The other terminal of the multimeter you should attach to each wire that you connect to the connector to the camshaft sensor. If no wire no electric current, the sensor is completely faulty.
– Now check the availability of electricity which must flow through the sensor loop. Take one contact of the multimeter and hold it to ground (any metal part on the engine). The other terminal of the multimeter you should attach to each wire that you connect to the connector to the camshaft sensor. If no wire no electric current, the sensor is completely faulty.
 – Have your helper start the engine
– Have your helper start the engine
 – Lean to one contact of the multimeter to one wire of the sensor of the camshaft, the other contact of the measuring equipment to the second sensor wire. Look at the display on the multimeter. Check the index specification specified in the manual of the car. In most cases, you will see an oscillating signal from 0.3 to 1 volt.
– Lean to one contact of the multimeter to one wire of the sensor of the camshaft, the other contact of the measuring equipment to the second sensor wire. Look at the display on the multimeter. Check the index specification specified in the manual of the car. In most cases, you will see an oscillating signal from 0.3 to 1 volt.
 – If no signal, the camshaft position sensor is faulty
– If no signal, the camshaft position sensor is faulty
Testing three-wire camshaft sensor
 – After you checked the wires to the camshaft sensor, the state of the connector, etc., and determined that your machine is equipped three-wire sensor SRM, it’s time to see if it works by multimeter. To do this, set the multimeter in the mode of “DC”.
– After you checked the wires to the camshaft sensor, the state of the connector, etc., and determined that your machine is equipped three-wire sensor SRM, it’s time to see if it works by multimeter. To do this, set the multimeter in the mode of “DC”.
 – Ask your assistant to turn the key in the ignition, but without starting the engine.
– Ask your assistant to turn the key in the ignition, but without starting the engine.
 One of the wires of the multimeter hold to ground (the metal bracket to the bolt or the metal part of the engine). The other wire of multimeter connect to the power wire of the sensor. Compare performance of the multimeter to the specification specified in the manual of the machine.
One of the wires of the multimeter hold to ground (the metal bracket to the bolt or the metal part of the engine). The other wire of multimeter connect to the power wire of the sensor. Compare performance of the multimeter to the specification specified in the manual of the machine.
 – Have your helper start the engine
– Have your helper start the engine

 – Connect the red wire of the multimeter to the red wire of the sensor and the black wire of the multimeter to the black wire of the sensor. Compare performance of the multimeter to the specification, which is specified in the repair manual for your car. If the indicator on the multimeter is lower than specified in the manual or data completely missing, then most likely the camshaft sensor has failed.
– Connect the red wire of the multimeter to the red wire of the sensor and the black wire of the multimeter to the black wire of the sensor. Compare performance of the multimeter to the specification, which is specified in the repair manual for your car. If the indicator on the multimeter is lower than specified in the manual or data completely missing, then most likely the camshaft sensor has failed.
 – Remove the camshaft sensor and check it for signs of physical damage or contamination.
– Remove the camshaft sensor and check it for signs of physical damage or contamination.
For example, the timing chain (or timing belt) may have an insufficient stretch or over-torqued. It is also possible worn belt tensioner or timing chain. Be careful!!!
When such problems with the machine can also cause malfunction may be a worn out timing belt. Because of this the camshaft and the crankshaft can lose synchronization. In the end, the camshaft sensor can send a wrong signal to the computer machine. In the end it will lead to inaccurate ignition and fuel injection.
