What is a decibel and how is it measured?
Decibel – what is it?

The decibel (abbreviated dB ) is the unit used to measure sound intensity. The decibel scale is a little odd because the human ear is incredibly sensitive. Your ears can hear everything from the touch of a finger to the skin to a loud jet engine. From the point of view of power, the sound of a jet engine is about 1 000 000 000 000 times stronger than the smallest audible sound by the human ear. It’s a big difference!
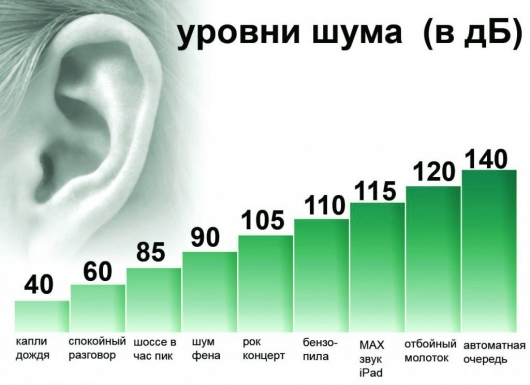
On a scale of decibel is the smallest, the smallest audible sound (almost total silence) is 0 dB. A sound 10 times more powerful is 10 dB already. A sound 100 times more powerful in almost complete silence, it’s been 20 dB. A sound 1,000 times more powerful than the almost complete silence is already at the level of 30 dB. Here are some common sounds and their decibel rating:
- Almost total silence – 0 dB
- Whisper – 15 dB
- Normal conversation – 60 dB
- Lawnmower – 90 dB
- Car horn – 110 dB
- A rock concert or jet engine – 120 dB
- A gunshot or firecracker – 140 dB
From my own experience you know that distance affects the intensity of sound – if you’re away, the strength is significantly reduced. All the above examples are taken from the calculation that you’re standing next to the sound source.
Any sound above 85 dB can cause hearing loss. Moreover, hearing loss is associated with both the power of sound and its duration.
For example, if you short time will hear a sound at 85 dB, you probably will not lose hearing. But if you listen to this loud sound for eight hours, it is likely that this sound will damage your ears.
Well, the impact of the sound is 140 dB will cause immediate damage to hearing (and will cause real pain).